Design Thinking, to innovate and transform too!
Design Thinking, this well-known method of the world of innovation is perfectly applicable to the problems of organization and operation. Transposed from innovation for products and services to cases of internal transformation, Design Thinking is a formidable efficiency: by putting the user at the heart of the reflection, the proposals are oriented “uses” and correspond to the expectations of the future users, guarantee of success and agility in the implementation. Inspired by IDEO this method whose founder sound Tim Brown says that it “can transform the way of developing products, services, processes and even strategy” is articulated in 5 steps.
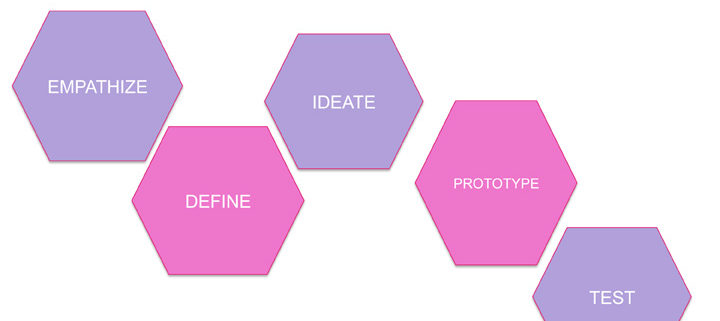
1. “Empathize”
The characteristic of Design Thinking is to be user oriented. It is about understanding the needs of the user, to put himself in his place to identify his “irritants”. Applied to the transformation empathy will allow to enter the fears but also the hopes of the employees and to identify the solutions that will emerge of themselves.
“The day a very young company, called Apple Computer, asked us for help to create a computer” for everyone “, we learned the value of empathy.” Tim Brown (IDEO founder)
2. “Define”
The next step is to clarify the needs through appropriate questioning, leave the traditional “how to do it” and move on to “why do it”. It is a question of re-questioning the initial problem and of reformulating it in a relevant way in relation to the sometimes unconscious needs of the target.
“A well-posed problem is half solved.” Albert Einstein
3. “Ideate”
To explore and create new possibilities, we must use what we call “divergent thinking”. Divergent thinking consists of multiplying options to create choices, that is, generating as many ideas as possible to increase the possibility of finding the right solution. There are many methods of creativity including brainstorming. Each brainstorming can have its own rules, but there is one rule that should be universal: to build from the ideas of others, not to judge others, to encourage the craziest ideas to feed a real creative speech of great richness.
“To get a good idea, you have to have many ideas first.” Linus Pauling, (Nobel Prize)
4. “Prototype”
Prototyping is a key step in the Design Thinking process; it is the demonstration by the proof. Realizing prototypes, sketching, modeling, modeling or building accelerates the progress of the project and allows to explore several ideas in parallel. By materializing an idea with an object, it can be easily evaluated, perfected and focused on the most appropriate solution. In the case of the service we imagine concrete implementations that result in action programs for immediate implementation.
“Prototyping is thinking with your hands. David Kelley (Ideo co-founder)
5. “Test”
Finally, the last “step” of the process is to test. Launching the project or prototype is the opportunity to learn by soliciting feedback from users and iterating about the product, service or experience designed. The error recovery principle is very powerful in terms of rapid design of relevant solutions. Feedback and feedback from users or consumers provides information that can open up new unsuspected markets that are far more promising and profitable. The same is true of internal transformation, rapid implementation in small steps promotes agility and commitment. “Fail early to succeed faster.” Tim Brown In conclusion, using Design Thinking to transform the company promotes in addition to concrete and immediate changes in strategy and process, the entry into a new culture of “permanent transformation“, mobilization of “collective intelligence” and ” agility “while ensuring a commitment from employees as actors of the solutions.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!